一.问题描述
设 X = <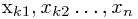 >是n个不同的实数序列,L的递增子序列L'= <
>是n个不同的实数序列,L的递增子序列L'= <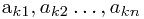 >,其中
>,其中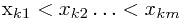 , 求最大的m值
, 求最大的m值
二.问题求解
2.1 转化为LCS问题求解
设序列A = <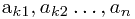 >是序列 X = <
>是序列 X = <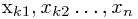 >按递增顺序排好的序列,则A与L的最长公共子序列为L的最长递增子序列。这样把求最长递增子序列问题规约为最长公共子序列问题LCS了。
>按递增顺序排好的序列,则A与L的最长公共子序列为L的最长递增子序列。这样把求最长递增子序列问题规约为最长公共子序列问题LCS了。
此解法的时间复杂度为: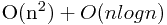
2.2 使用动态规划求解
设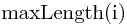 为X中以
为X中以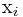 为末元素的最长递增子序列的长度,有如下的递推方程:
为末元素的最长递增子序列的长度,有如下的递推方程:

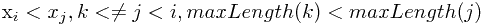
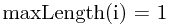
即在求以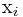 为末元素的最长递增子序列长度时,对所有在
为末元素的最长递增子序列长度时,对所有在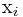 前面的元素
前面的元素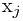 ,且
,且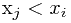 ,如果j的值存在,找出
,如果j的值存在,找出 的最大值,则
的最大值,则 ,否则
,否则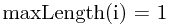
算法如下:
function lis_length( a )
n := a.length
q := new Array(n)
for k from 0 to n:
max := 0;
for j from 0 to k, if a[k] > a[j]:
if q[j] > max, then set max = q[j].
q[k] := max + 1;
max := 0
for i from 0 to n:
if q[i] > max, then set max = q[i].
return max;
程序如下:
/*
**Descrition: Returns the length of the longest increasing subsequence
** Note that this is looking for the longest strictly increasing subsequence
** This can be modified for other situations
**Author: jia1546@163.com
**Date: Oct 15, 2011
**Version: 1.0
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int lis(int *a, int n)
{
int i, j;
int *best, *prev;
int max = 0;
best = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * n);
prev = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * n);
for(i=0; i<n; i++)
{
best[i] = 1;
prev[i] = i;
}
for(i=1; i<n; i++)
for(j=0; j<i; j++)
if(a[i] >= a[j] && best[i] < best[j] + 1)
{
best[i] = best[j] + 1;
prev[i] = j;
}
for(i=0; i<n; i++)
if(max < best[i])
max = best[i];
free(best);
free(prev);
return max;
}
int main()
{
int n;
int *array;
int i;
while(scanf("%d",&n) != EOF)
{
array = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * n);
for(i=0; i<n; i++)
scanf("%d",array+i);
printf("# of the lis is: %d\n", lis(array, n));
}
return 0;
}
时间复杂度: 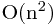
2.2 改进的动态规划
在上一算法中,在计算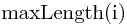 时,需要找出最大的
时,需要找出最大的 ,由于
,由于 无序,所以只能顺序查找
无序,所以只能顺序查找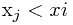 的最大值
的最大值 ,如果能让
,如果能让 有序,可以使用二分查找的方法降低复杂度到
有序,可以使用二分查找的方法降低复杂度到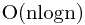
数组M[j]存储所有长度为j的子序列中最小末元素的X[k]的下标k
数组P[k]存储以X[k]为末元素的最长递增子序列中X[k]的前一元素的位置
算法如下:
L=0
for i=1,2,...n
binary search for the largest positive j<=L
such that X[M[j]] < X[i](or set j=0 if no such j exists)
P[i] = M[j]
if j == L or X[i] < X[M[j+1]]
M[j+1] = i
L = max(L, j+1)
程序如下:
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
/* Finds longest strictly increasing subsequence. O(n log k) algorithm. */
void find_lis(vector<int> &a, vector<int> &b)
{
vector<int> p(a.size());
int u, v;
if (a.empty()) return;
b.push_back(0);
for (size_t i = 1; i < a.size(); i++)
{
// If next element a[i] is greater than last element of current longest subsequence a[b.back()], just push it at back of "b" and continue
if (a[b.back()] < a[i])
{
p[i] = b.back();
b.push_back(i);
continue;
}
// Binary search to find the smallest element referenced by b which is just bigger than a[i]
// Note : Binary search is performed on b (and not a). Size of b is always <=k and hence contributes O(log k) to complexity.
for (u = 0, v = b.size()-1; u < v;)
{
int c = (u + v) / 2;
if (a[b[c]] < a[i]) u=c+1; else v=c;
}
// Update b if new value is smaller then previously referenced value
if (a[i] < a[b[u]])
{
if (u > 0) p[i] = b[u-1];
b[u] = i;
}
}
for (u = b.size(), v = b.back(); u--; v = p[v]) b[u] = v;
}
/* Example of usage: */
#include <cstdio>
int main()
{
int a[] = { 1, 9, 3, 8, 11, 4, 5, 6, 4, 19, 7, 1, 7 };
vector<int> seq(a, a+sizeof(a)/sizeof(a[0])); // seq : Input Vector
vector<int> lis; // lis : Vector containing indexes of longest subsequence
find_lis(seq, lis);
//Printing actual output
for (size_t i = 0; i < lis.size(); i++)
printf("%d ", seq[lis[i]]);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
Ref
http://www.algorithmist.com/index.php/Longest_Increasing_Subsequence